Méningiomes-Fiche practical radiotherapy written by Dr Adrien Peace, radiotherapist
Warning: The radiotherapy decision is taken jointly by the radiotherapist and the neurosurgeon in a multidisciplinary consultation meeting.
Sheet written by Dr. Adrien Peace, oncologist-radiotherapist, practicing at the Bobigny Radiotherapy Institute and involved in the management of brain tumors in collaboration with the neuro-oncology service of Saint-Louis Hospital and the neurourgy services of Lariboisière, Beaujon and the Ophthalmology Adolphe Foundation of Rothschild.
See press article " Two new
radiotherapists for the Bobigny Radiotherapy Center" See the biography of Adrien Peace here
If necessary, making an appointment with this doctor is possible via his secretariat on 01 41 50 57 10.
Big thank you to Dr Adrien Paix for his availability and his work for the association.
Méningioma radiotherapy
information sheet
The sheet in PDF format can be downloadable here
Generalness
Radiotherapy is a treatment mode using rays, most often high energy photons (or X -rays), targeting meningioma and whose objective is to destroy meningioma cells. The rays used are invisible and painless.
The rays are produced from a radiotherapy machine that can be:
 |
 |
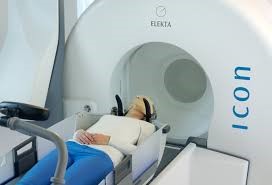 |
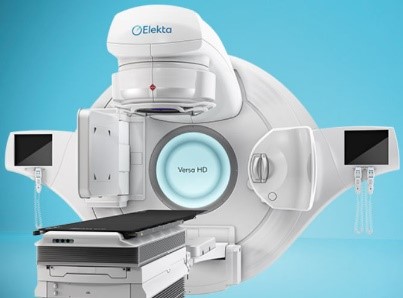
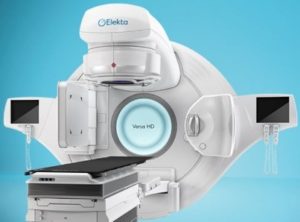
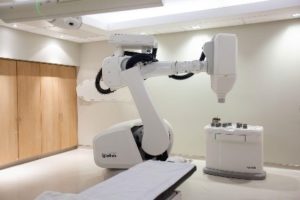
| Linear accelerator | Robotic linear accelerator: Cyberknife® | Gammaknife® |
Each machine allows a special treatment technique
- Linear accelerators allow treatments in conformational radiotherapy and dynamic arc therapy with intensity modulation: in this case the head of the machine delivers the rays by touching (by forming an arc) around the patient and adapting the shape of its beam as a function of the treatment angle so as to "mold" the dose deposit around meningiom.
- Robotic linear accelerators allow a more precise and more targeted treatment of meningioma. They are used for so -called "stereotaxis" or "radiosurgery" irradiation techniques consisting in delivering a dose per larger session and with a lower number of session than in the case of conventional treatment techniques. This technique is generally reserved for small meningomes. Some non -robotic linear accelerators also allow stereotaxy treatments.
- Gammaknife also allows stereotaxy or radiosurgery treatments . Its particularity is in particular of necessity most often the installation of a stereotaxis framework and to use to produce its rays of radioactive cobalt sources.
Radiotherapy techniques
TRI -dimensional conformational radiotherapy (3D)
Several fixed rays beams are used to target meningioma and their shape is suitable for the shape of meningioma. We can vary the intensity of the beams in order to obtain a more precise dose deposit in the meningioma level, we speak in this case of conformational radiotherapy with intensity modulation.
Dynamic arc radiotherapy with intensity modulation (AVMI or VMAT)
Unlike the dimensional sorting conformational radiotherapy, the rays are delivered by the machine while it is in motion. It performs circular rotations around the patient in the form of an arc and adapts the shape of the beam throughout the arc. As a result, the dose is more precisely delivered to the tumor.
Tomotherapy
Tomotherapy is close to AVMI with the difference that instead of turning around the patient in the form of an arc, the radiotherapy machine revolves around the patient in the form of a propeller.
Stereotaxic radiotherapy or radiochuruse
Stereotaxis or radiosurgery radiotherapy makes it possible to deliver larger doses of rays in small volumes and in a small number of sessions (hypofractional treatment). This technique is particularly suitable for grade i and small meningiomas.
Proton therapy
This particular treatment technique uses protons as particles instead of photons used by other techniques. This treatment modality makes it possible to better save healthy tissues. As part of meningioma, clinical gain is not yet formally demonstrated, moreover this technique is not available in France with only three centers.
Treatment
Initial consultation
During a consultation, the duration of which varies from 20 to 45 minutes, you meet your referring doctor. This will question your personal and family history, the treatments you take and take stock of the history of your illness.
After a clinical examination, he will explain the course of radiotherapy, his objectives and any side effects.
This consultation is an opportunity for you to ask the questions you may have about your illness or the treatment offered.
At the end of this consultation, your doctor will offer you the realization of a simulation scanner which can possibly be supplemented by an MRI.
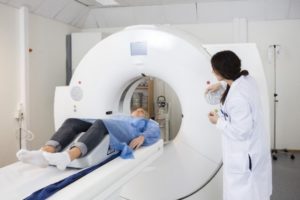
The simulation scanner
| Before carrying out the simulation scanner there is no specific preparation required.
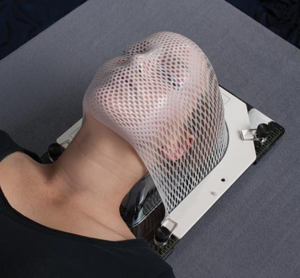
The radiotherapy manipulator installs you on the scanner table in the same position as the one you will have for treatment sessions. In order to make sure you always stay in the same position, a personalized mask will be made.
|
 |
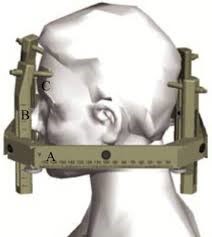
In some cases the helmet can be replaced by a frame which will be screwed on the head after local anesthesia
Once the scanner is made, it will be used by your doctor to program your treatment.
Example of thermoformed mask
Example of stereotaxis framework
Dosimetry
Once the simulation scanner has been completed, your doctor will define the areas to be treated but also the healthy organs to protect. To do this, it follows the recommendations of international learned companies so as to offer you the highest quality treatment and in the best safety conditions.
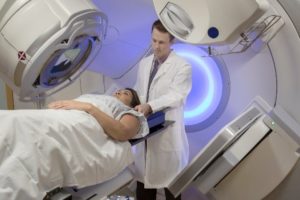
Treatment sessions
 |
The number of treatment sessions varies according to the radiotherapy technique used, which itself depends on several parameters including the size of meningioma, its location and its grade.
When you arrive, the radiotherapy manipulator invites you to prepare in your locker room and then install you under the radiotherapy machine in the same position as during the simulation scanner.
|
Images will then be made to ensure that you are perfectly positioned. The doctor then gives agree to carry out the processing session. The duration of each session is about ten minutes.
Throughout the duration of the treatment, you see your doctor in consultation once a week. This is an opportunity for your doctor to assess any side effects, and for you to ask the questions you may have.
Side effects
During treatment
Fatigue
A slight fatigue during treatment is possible. It is not necessarily linked to treatment or disease but is most often linked to frequent and potentially long travel.
Advice :
- Do not hesitate to take a nap when you feel the need.
- Keeping regular suitable physical activity makes it possible to limit fatigue.
- Be sure to observe a good lifestyle: limit exciting (coffee, tea), respect minimum sleep schedules, limit exposure to screens.
Headache (headache)
Sometimes present before the start of radiotherapy, they can be increased during radiotherapy. They are linked to reaction edema due to inflammation. They are often well controlled with drugs (corticosteroids, paracetamol).
Advice :
- Talk to your doctor as soon as they occur, effective treatment may be prescribed.
Nausea - Vomiting
Nausea can also occur during treatment. Rarely important, they can be easily calmed by drug treatments.
Advice :
- Talk to your doctor as soon as they occur, effective treatment may be prescribed.
- Remember to drink enough so as not to dehydrate yourself.
- Avoid foods that are difficult to digest (fatty foods, sauce dishes, etc.)
Epilepsy attacks
Sometimes present before radiotherapy, they can repeat themselves during treatment. They can be generalized: the patient loses consciousness and presents tremors of the whole body. If the crisis lasts more than 5 minutes it is necessary to call the SAMU (15); They can be partial and have various symptoms such as the tremor of one hand, visual or auditory hallucinations ...
In any case, you should talk about it with your doctor so that it adapts your antiepileptic treatment in the event of a crisis.
Advice :
- If the crisis lasts more than 5 minutes, call the SAMU (15)
- As soon as a crisis is talking to your doctor
- Avoid any potentially at risk in the event of a crisis (driving, swimming, etc.)
- Avoid favorable factors: lack of sleep, exciting, prolonged exposure to screens
Hair loss
Hair loss occurs 2 to 3 weeks after starting treatment and only concerns the treated area. In addition, the hair grows in the majority of cases within 2 months. Hair loss is much less significant or even absent in the event of stereotaxic radiotherapy or radiosurgery.
A hair prosthesis (wig) may be prescribed by your doctor.
Advice :
- You can ask your doctor to prescribe a hair prosthesis (wig), it is reimbursed by social security
- Avoid colorations
After treatment
Side effects can last several days/weeks after the end of treatment without it being abnormal. In case of concern do not hesitate to tell your doctor about it.
Side effects can occur several months after the end of treatment:
- Radionecrosis : This is a complication linked to the irradiation of normal brain cells, in contact with the tumor. Often asymptomatic, it can sometimes manifest itself in the same symptoms as those present before treatment. Your doctor can make it the diagnosis with suitable imaging and if necessary offer you a treatment.
- Memory disorders : Modern radiotherapy techniques avoid brain areas responsible for memory. However, when a large volume of the brain is irradiated, it is possible to have more difficulty remembering certain things after 6 to 12 months.
Monitoring and monitoring
After the end of your treatment, your doctor will see you in consultation to explain the methods of evaluating the efficiency of treatment and surveillance. These most often require the realization of MRI.
Méningiomes-Fiche practical radiotherapy written by Dr Adrien Peace, radiotherapist