Méningiomes: Inform patients of the risks involved with the taking of Androcur and progestins (Luteran, Lentenyl, etc.)
Risks involved with the taking of Androcur and progestins (Lotéran, Lotényl, etc.)
Meningioma is a benign tumor of the envelope of the nervous system, that is to say the meninges which are the envelope of the brain and the spinal cord. It is a fairly frequent disease. Rather, it affects adults over 50 with a female predominance, since we know that some meningiomas can have progesterone receptors (and more rarely to estrogens).
Meningioma is a tumor developed at the expense of the meninges:
- Meningioma can therefore be located inside the skull, in contact with the brain, the cerebellum, the spinal cord or at the root of a nerve.
- Meningioma represents 20 % of intracranial tumors, not to mention brain metastase tumors.
- There are a wide variety of intracranial tumors: some are malignant and other benign. Meningioma is a tumor most often benign.
- We have not found any causes for the development of meningioma although some family cases have been described.
- Meningioma is often a unique tumor. When there are several, it is a strong indication that this meningimatosis is due to drugs.
- The prognosis for meningioma depends on its size and location.
- The size of meningioma depends on the precocity of its discovery.
Example: frontal meningioma (located at the front in the skull) can reach more than ten centimeters because it does not generate any symptoms before having reached this size.
The symptomatology of meningioma depends on its location:
- When the meningioma is located inside the skull, the symptoms appear from large meningioma:
- Headache resistant to simple anti-them-powers;
- vomiting;
- confusion, fatigue;
- Motor and sensitive disorders depending on the right or left location of the tumor in contact with the brain: numbness of members see deficit (hemiplegia, either paralysis of the right or left of the body), language disorders, body diagram, etc.;
- dizziness and loss of balance;
- Movement coordination disorder;
- epilepsy.
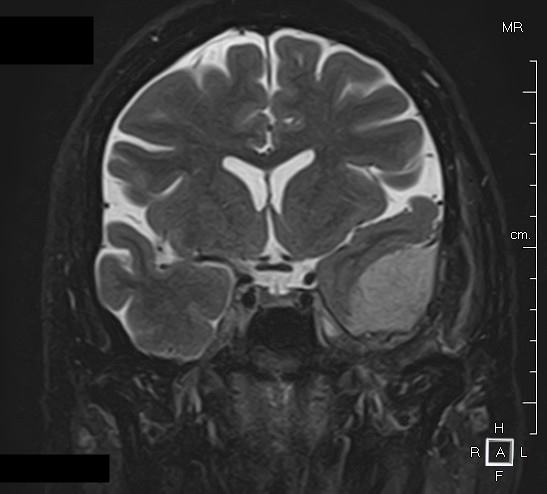
- When the meningioma is located in contact with a nerve: loss of smell, loss of sight, deafness, disturbances of the hormonal secretions of the pituitary gland, pain and facial paralysis. Examement: it is necessary to better carry out an MRI with injection of contrast product. This examination makes it possible to quantify the edema present around the lesion, many a scanner.
Risks involved with the taking of Androcur and progestins (Lotéran, Lotényl, etc.)
Méningiomes: Inform patients of the risks involved with the taking of Androcur and progestins (Luteran, Lentenyl, etc.)
Find the other Amavea articles here