Meningioma: monitor or operate?
Benign tumor, meningioma is all against the brain, and near the nerves. Explanations from Dr. Raftopoulos, neurosurgeon.
Note from the association: It is interesting to note that, in this recent article of a Belgian newspaper, there is still no mention of the responsibility of certain progestins in the occurrence of meningiomas, even though the EMA (European Medicines Agency) has been informed since 2019, and then informed all European countries….
Posted on 11-10-2022 at 07:00
/cloudfront-eu-central-1.images.arcpublishing.com/ipmgroup/E6NY4NWKZFEBRDLYW5CVJ3M46M.jpg)
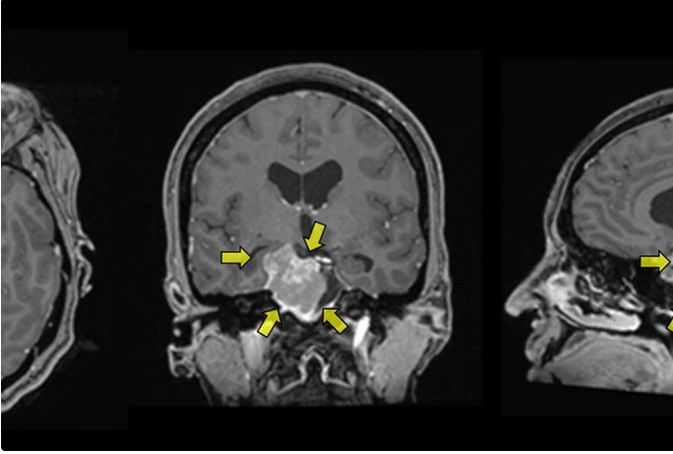
It is less common than breast, lung or colon cancer ... but meningioma is not so rare . " It is a tumor that develops in the meninges, the envelopes of the central nervous system ," said Professor Christian Raftopoulos, a neurosurgeon at the Saint-Luc university clinics. The tumor starts from the arachnoid, which envelops the whole brain, the spinal cord and the initial part of the nerve roots . In 80% of cases, the tumor is benign.
This tumor is slowly developing from the envelope to the nephew system, which it will compress. Most often benign and very slow growth, the tumor is sometimes discovered by chance, at the turn of an MRI of control, for headaches for example. “ It also happens that we discover a meningioma after an epilepsy crisis. In this case, as it is he who irritates the cerebral cortex, the operation can delete epilepsy. ""
What treatment?
These incidental meningiomas, discovered "by chance" during a control exam, remain stable in 50% of cases. " I am several patients for meningiomas that do not grow " recognizes Professor Raftopoulos. In these cases, there is no treatment, just a control.
But if the meningioma pushes and compresses the nervous system, we will decide to operate it. “ All the art of surgery is to remove a maximum of this meningioma by causing as few sequelae as possible . »»
Remove the maximum, why? “ To reduce the risk of recurrence. Sometimes there are even when you think you have removed everything. But the complete excision, for a benign tumor, does not make sense if it induces significant deficits. It is better to leave a small residue which will eventually be treated by radiotherapy. The operation is delicate . “The most difficult is when a meningioma wraps nerves. We could reach the nerve of hearing, that of swallowing ... and provoke a handicap. It is a long -term job, surgery of several hours. Taking back the brain meningioma is difficult. But it is even more difficult to take off the tumor from the cranial nerves without damaging them. ""
The neurosurgeon explains that if the residue - which is 5 to 10% of the initial tumor - tends to push, we can do stereotaxic radiotherapy, which makes it possible to burn residues and control the disease in an extremely prolonged manner.
We analyze the tumor
After removing the tumor, we analyze it. “ A classic analysis, under a microscope, with dyes. Then a molecular biology, where you are looking for mutations in certain genes. We regularly see in the meningiomas a mutation of the NF2 gene. It is interesting to know, for future gene therapies . »»
An analysis showing that meningioma is aggressive will lead to closer surveillance and often radiotherapy in the weeks following surgery. “ But radiotherapy has controversial efficiency. It happened to me to operate a patient several times, who had a grade 2 meningioma, who repeatedly rejected , despite radiotherapy treatment. ""
What is meningioma?
What is the impact?
There are 9 meningiomas is for 100,000 people, where breast cancer has 125 out of 100,000.
The age
It is between 50 and 60 years that there are the most cases. Twice as many women as men " probably for genetic reasons ," said Dr. Rafotopoulos.
Benign
In 80% of cases, the lesion is benign. “ There are three grades. In 80% of cases, it is a benin grade 2. In 18%, it is an intermediary grade 2, with signs of aggressiveness. And in less than 2%, there are aggressive meningiomas. In this case, the neurosurgeon will have to be as radical as possible in his excision . »»
Where is meningioma?
There are intracranial meningiomas and intrarachidian meningiomas. At the intracranial level, there are supantial (upper parts of the brain) and subtential (under the tent of the cerebellum). Those who are in the posterior pit or the base of the skull are more difficult to operate, because all the cranial nerves are there. “ Meningioma can wrap them, and it is an even more delicate operation . »»